The spinal cord is the body’s main nerve trunk. It is a bundle of nervous system and supportive cells that extends from the base of brain. In order to transmit electrochemical signals, there are about 13,500,000 neurons in the spinal cord. Central Nervous system is composed of spinal cord and brain.
It is around 45 cm (18 in) in men and around 43 cm (17 in) long in women. Also, the spinal cord has a varying width, ranging from 1/2 inch thick in the cervical and lumbar regions to 1/4 inch thick in the thoracic area.
The spinal cord functions primarily in the transmission of neural signals between the brain and the rest of the body but also contains neural circuits that can independently control numerous reflexes and central pattern generators.
The spinal cord has three major functions as a conduit for motor information, which travels down the spinal cord, as a conduit for sensory information in the reverse direction, and finally as a center for coordinating certain reflexes.
The spinal cord is protected by three layers of tissue, called spinal meninges that surround the canal. The dura meter is the outermost layer, and it forms a tough protective coating. Between the dura mater and the surrounding bone of the vertebrae is a space called the epidural space. The epidural space is filled with adipose tissue and it contains a network of blood vessels. The archnoids materis the middle protective layer.
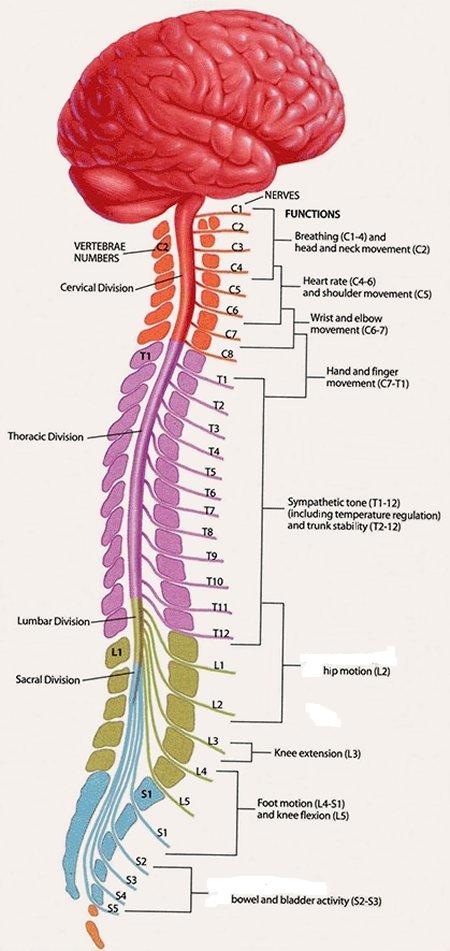
The human spinal cord is divided into 31 different segments. At every segment, right and left pairs of spinal nerves (mixed; sensory and motor) form.
The spinal cord is supplied with blood by three arteries that run along its length starting in the brain, and many arteries that approach it through the sides of the spinal column. Connecting with the cord are 31 pairs of these spinal nerves, which feed sensory impulses into the spinal cord, which in turn relays them to the brain.
A baby can lose about half of their nerve cells before they are born.
The spinal cord can actually work independently of the brain, sending out responses to the muscles directly.The spinal fluid in it acts as a cushion to protect the cord from damage.



