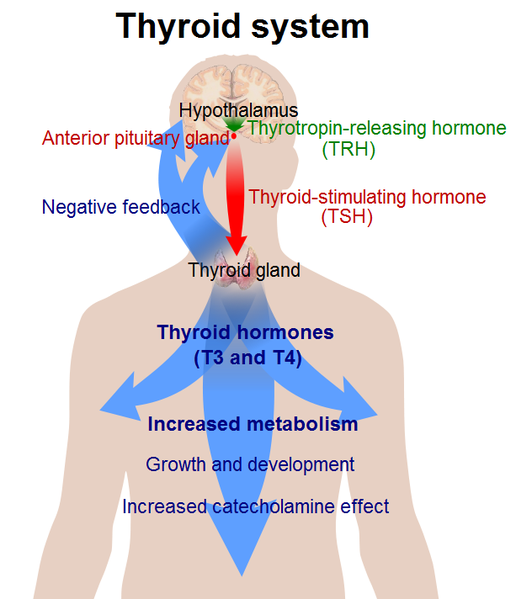
Thyroid is a small gland situated at the front of your neck, just below the larynx about the size of two joined cherries. It is controlled by the pituitary gland, which is the master gland for all other glands and hormones in our body.
The thyroid gland releases 3 important hormones- Tri-iodothyronine (T3), Thyroxine (T4) and Calcitonin. These hormones play a prominent role in controlling the entire body’s metabolism rate by circulating into the blood and stimulating cells to convert more glucose.
If the thyroid gland secretes a little amount of Tri-iodothyronine and Thyroxine, then we will get cold or tired, our skin gets dried and we will put on weight.
If the thyroid sends out too much of T3 and T4 hormone, then it causes anxiety, sweaty and overactive and we will also lose weight.
The amount of T3 and T4 send out by the thyroid depends on how much thyroid-stimulating hormone is sent to it from the pituitary gland.
If the amount of T3 and T4 drops out in the blood, then the pituitary gland sends out extra thyroid stimulating hormone to tell the thyroid to produce more.
It also regulates the heart rate, blood pressure and body temperature.
It is also responsible for calcium in the body.
The thyroid cells are the only cells to absorb iodine. Over iodine intake leads to increased secretion of hormones in thyroid gland which brings lot of disorders in the metabolism rate.
Read more:
http://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/bhcv2/bhcarticles.nsf/pages/thyroid_gland_explained



